gis
If you were to derive each of these inputs on your own, this is how you would do it. However, we’ve just provided these for you in this lab. In other words, the below is FYI (you don’t have to do this).
Input Data
The ungulate utilization model requires:
- A drainage network layer
- A water body and springs layer
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
- Vegetation type (by species) raster data
Existing, readily and freely available GIS datasets from GIS data clearinghouses can be used as model inputs. For the pilot study ungulate utilization model, we used:
-
NHD+ for a drainage network layer & hydrography data
-
- National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) Plus
- Both stream and water body data
-
Landfire for Vegetation Type raster data
-
- Us_110evt (existing vegetation type)
-
USGS Digital Elevation (DEM) data for Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
-
- USGS NED 10 m DEM data
These data were processed to generate the following raster datasets:
Euclidean distance to Water (NHD streams and water bodies), Forage preference (LANDFIRE landcover data), Percent slope map (based on USGS 10-m DEM)
Vegetation Input Derivation
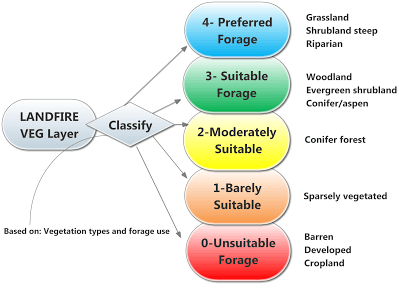
How the LANDFIRE land cover data for existing (2008) was classified by ungulate forage preferences established in the literature.
Task 1: Classify the LANDFIRE land cover data
- Step 1: Load LANDFIRE land cover type raster: Us_110evt.img (existing land cover type)
- Step 2: Export the Existing LANDFIRE Raster as Grazing_Veg_Capacity.img
- Step 3: Add a new field to Grazing_Veg_Capacity.img and name it “Code” to represent ungulate grazing preferences (0-4) (Table 4).
- Step 4: Assign the ungulate land cover preferences (0-4) to the field named “Code” based on Table 2 using field SAF_SRM in Us_110evt.img
Table 4. Suitability of LANDFIRE land cover classes for ungulate grazing
O - Unsuitable - LANDFIRE land cover = Cropland, developed, roads, barren, or water.
1 - Barely Suitable - LANDFIRE land cover = sparsely vegetated.
2 - Moderately Suitable - LANDFIRE land cover = conifer forest.
3 - Suitable - LANDFIRE land cover = woodland or evergreen shrubland.
4 - Preferred - LANDFIRE land cover = grasslands, scrubland steep or riparian.
- Step 5: Use the raster to ASCII command to convert the .img raster to an ASCII raster for use in MATLAB.
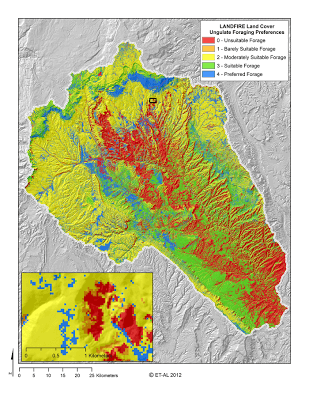
Your classified output should look something like the above for the Escalante (click on image for larger view).
**Output file: **
- Grazing_Veg_Capacity.img
- Grazing_Veg_Capacity.asc
Slope Input Derivation
Task 1: Create a project area slope map
- **Step 1: **Open the 10 m DEM in ArcMap
- Step 2: Generate a slope map using the Slope Tool (ArcToolbox under Spatial Analyst Tools -> Surface). Use the Percent option for the output measurement.
- Step 3: Use Extract by Mask with your project area boundary layer to confine the slope map to the project area.
- Step 4: Use the raster to ASCII command to convert the .img raster to an ASCII raster format for use in MATLAB.
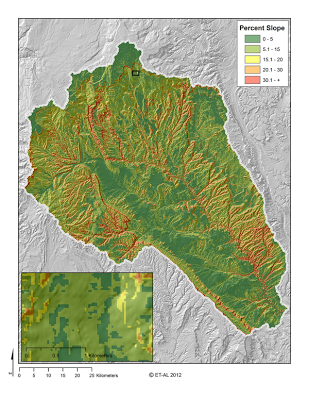
Your slope analysis should look something like the above.
**Output files: **
- Ungulate_Capacity_Slope.img
- Ungulate_Capacity_Slope.asc
Distance to Water Source Input - Derivation
Task 1: Convert NHD waterbodies to polyline (for distance to water input.)
- Step 1: Use the Polygon to Line command as follows:
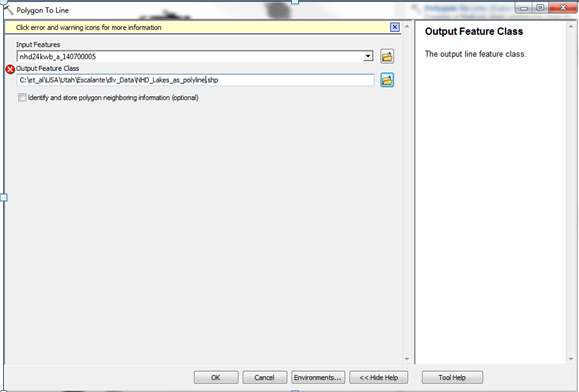
**Output: **
-
NHD_Lakes_As_Polyline.shp
-
Step 2: Use the Merge command to combine the resulting lakes polyline with the NHD perennial streams include streams outside your project area.
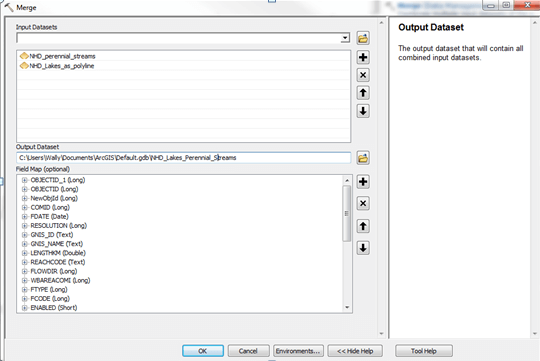
**Output: **NHD_Lakes_Perennial_Streams.shp
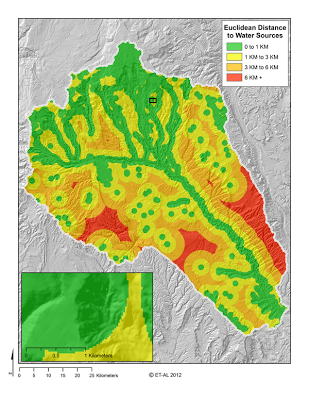
**Task 2: Use the Euclidean Distance command to calculate distance to water sources **
- **Step 1: **Load the input layer, which is the layer that was generated in the previous task NHD_Lakes_Perennial_Streams
- **Step 2: **Assign an output grid name
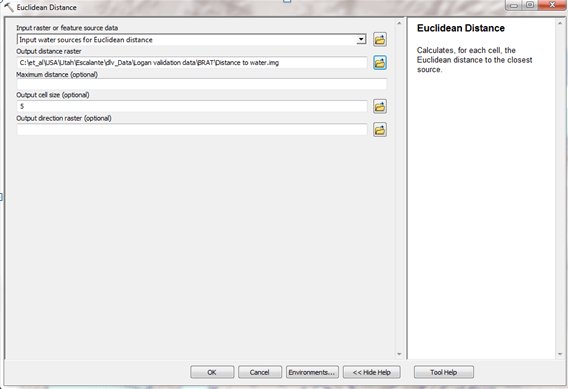
Output:
-
NHD_Lakes_Streams_For Euclidean_Distance.img
-
Step 3: Clip the output raster NHD_Lakes_Streams_For Euclidean_Distance.img by your area of interest.
Use Extract by Mask
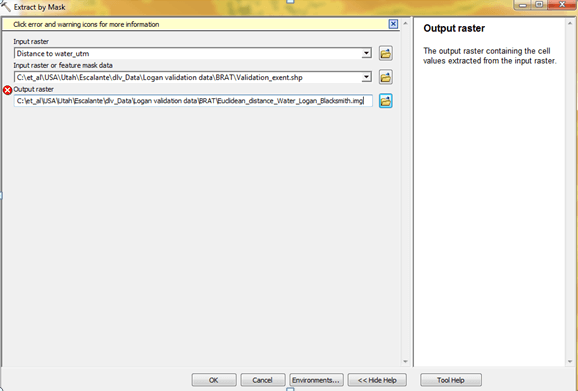
Step 4: Convert raster to ASCII raster using the Raster to ASCII command.
Your euclidean distance should look something like the above.
Output:
- Euclidean_Distance_to_Water.img
- Euclidean_Distance_to_Water.asc